Actinology –
- Actinium (n.) – Formed by Greek aktis or actino, “pertaining to rays” combining with the chemical suffix -ium. Actinium is a radioactive element discovered in 1899.
Aerology –
- Aerobacter (n.) – type of bacteria widely spread in the air.
- Aeroplane – aero (air) plus Greek planos (wandering). Aeroplane means a vehicle that wanders in the air.
Agrology –
- Agronomy – The science of land management and crop production. formed by agros plus nomos, “to arrange”.
- Agromania – An intense desire to be alone in the open. Formed by Agros, “an open place” plus mania, “an irresistible desire to do something”.
Agrostology –
- Agrostography – The description of grasses. Formed by agrostis plus Greek graphein, meaning “to write, to describe, to draw”.
Algology –
- Algaecide – A substance that kills algae. Formed by Latin alga plus Latin cīda, “killer” from Latin caedo, “kill”.
Andrology –
- Andromania – Extreme sexual desire in female towards male. Formed by mania meaning extreme obsession, with andros meaning man “male”.
- Androgen – Androgen is a sex hormone. The hormone that is produced in male. It is formed by andros plus Greek genes, “give birth”.
Anthropology –
- Anthropogeny – Origination or evolution of the human race. Formed by anthropos plus genesis meaning “origin”.
- Philanthropy – The love for human beings. Formed by Greek Philos meaning “dear, love”, plus anthropos meaning “human”.
- Misanthropy – Hatred for human beings. Formed by Greek misein, “to hate” with anthropos.
- Anthropocentric – The fact that man is in the centre of a reaction. Formed by anthropos plus Greek kentron, “centre”.
Apiology –
- Apiculture – The cultivation of bees. From Greek apis, “bee”, plus Latin cultura “a cultivating, agriculture”.
Archaeology –
- Archaic – Extremely old.
- Archaeopteryx – Archaeopteryx is the oldest known bird living during the late jurassic along with dinosaurs. Formed by archaios plus Greek pteron meaning “wings”.
Audiology –
- Audiophile – One who has interest in producing high-fidelity sound. Formed by Latin audire, plus Greek Philein, “to love”.
Bacteriology –
- Bacteriophage – The word bacteriophage literally means the eater of bacteria. As its root lies in the Greek word phagein, “to eat”. Bacteriophages are virus that destroy bacteria.
Bioecology –
- Biology – The scientific study of living organisms and their vital processes. From Greek bios, “life”.
- Ecology – The study of how organisms interact with their environment. From Greek oikos “house, dwelling place, habitation, environment”.
Biology –
- Biography – The description of one’s life. Formed by Greek bios, plus graphein, “to write, to draw, to describe”.
Cardiology –
- Electrocardiography (ECG) – It is a recording of heart’s electrical activity.
Craniology –
- Craniography – The description of skulls. Formed by Cranion plus graphein, “to write, to draw, to describe”.
-
- Craniometry – The science of measuring the skull to determine their characteristics relationship with body type, sex, genetic population etc. Formed by Cranion, plus Greek metron “measure”.
And a Craniometer is an instrument to measure the dimension of skulls.
- Craniopagus – The condition of Siamese twins joined at the head. Formed by Cranion plus Greek pagos “fixed, set”.
Criminology –
- Accriminate – to accuse someone of an offence. Formed by ac “to”+ criminate “accuse”
Cryology –
- Cryogen – That produces freezing temperature. Formed by kryos plus Greek gene, to give birth. Cryogenic is the adjective. Cryogenic fuels are used in cryogenic missiles.
-
- Cryolite – A colourless mineral; sodium aluminium fluoride (Na3AlF6). Formed by kryos plus Greek lithos meaning stone. So, cryolite literally means – a freezing stone.
Actually large deposits of this mineral are found in Greenland, a place where the temperature doesn’t exceed 10°C.
Cynology –
- Canine – Adjective for dog; dog-like. We have 4 pointed conical dog-like teeth called canine.
- Cynodon – Commonly known as Bermuda grass or dog’s tooth grass. From Greek kyon, plus odous, “tooth”
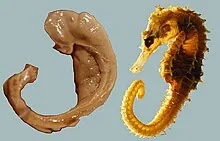
- Cynopterus – A genus of megabats. From Greek kyon, “dog” plus, ptron, “wing”. Literally, cynopterus means “flying-dog”, as the megabat resembles the dog in the shape of its head and mouth. See images.
Cytology –
- Cytoplasm – the contents of a cell except for the plasma. Latin plasma “mold”. So cytoplasm literally means “something that forms something”.
Dendrochronology –
- Rhododendron – An evergreen shrub cultivated for its profuse handsome flower. Formed by Greek rhodon “rose”, plus dendron “tree”. So, etymologically rhododendron means “rose-tree”.
Dendrology –
- Dendrophilous (adj.) – animals living in trees are called dendrophilous animals; arboreal.
Dermatology –
- Epidermis (n.) – the outer skin. Greek epi means “on”.
- Ectoderm (n.) – same as epidermis – the outer skin. Greek ektos means “outer”.
- Mesoderm (n.) – the middle layer of the skin. Formed by Greek mesos, middle plus derma, “skin”.
- Endodermis (n.) – the innermost layer of the skin. Formed by Greek endon, meaning “inner or within”.
- Dermatitis (n.) – Inflammation of the skin. Greek -itis means “Inflammation”.
Ecology –
- Eco-friendly – Not damaging to the environment.
- Economy – The art of managing a household. Formed by Greek oikionomicos, “management of a house or a family”.
Embryology –
- Embryogenesis – The process by which an embryo is formed. The Greek word genesis means birth or formation.
Endocrinology –
- Exocrine glands – Gland that secretes hormone externally through a duct. Greek exo “external or outer”.
- Autocrine (adj.) – Of or relating to a substance that is secreted by a cell and acts on the same cell. Formed by Greek autos “self”.
Entomology –
- Entomophagous – insectivorous; an animal that feeds on insects. Formed by Greek entomon plus phagos meaning “eater of” from phagein (to eat).Phagein has a Proto Indo-European root i.e. bhaga, meaning “to share out; to get a share; apportion”.
- Entomolite – Fossilized insects. Formed by entomon with Greek lithos, “stone”.
- Anatomy – The study of the structure and function of the body of an organism. Formed by ana, “up”; plus temnein, “to cut”. So anatomy literally means “the cutting up”. See the picture of human anatomy.
- Epitome – The summery of a written work, an abstract. Also refers to a person or thing that is a perfect example of a particular quality or type. Formed by Greek epi, “into” plus temnein.
Epitome literally means a cut piece from a bigger thing.
- Atom – A hypothetical indivisible extremely minute body, that is the building block of the universe. Comes from Latin atomus, “indivisible particle” from Grek atomos “uncut”; from a- meaning “not” and temnein “to cut”.
So, atom literally means the smallest particle that cannot be cut further.
- Diatom – A microscopic unicellular algae. From Greek diatomos to Latin diatoma to English diatom. Formed by Greek dia, meaning through, plus temnein “to cut”. So, diatom means “to cut through”.
If you cut through anything, you’ll get two pieces of it. Therefore diatom literally means cut into two. So named because they typically appear to have cut in two halves. See pictures.
- Dichotomy – Cutting in two; being twofold; a classification into two. From Greek dichotomia, meaning “cut into two”; from dikha meaning “two”, plus temnein.
- Temple – A building for worship. Formed by temnein (to cut); literally means a place that is cut off. Figurative sense of “a place occupied by divine presence.”
- Contemplate – reflect upon, study, ponder, meditate etc. Formed by Latin prefix com- meaning together, plus Latin templum, meaning an area of taking of auguries. So, to contemplate literally means “to mark out a space for observation” (as an augur does).
Epidemiology –
- Epidemic (n.) – a widespread outbreak of an infectious disease; many people are infected at the same time.
- Pandemic (n.) – An epidemic that is geographically widespread; occurring throughout a region or even throughout the world. From pan meaning “all” (As in pangia); plus demos “people”.
- Endemic (adj.) – Formed by en “in”; plus demos “people”. Endemic has several meanings –
I. A disease constantly present in a particular locality.
Use: Endemic malaria. A disease endemic to the tropics.
II. (In Ecology) Native to or confined to a certain region.Use: The islands have number of endemic species.
Epistemology –
- Epitaph – An inscription on a tombstone. Formed by Greek epi, “on or over” with taphos, “tomb, burial”.
Ethology –
- Ethics – The study of morals. Originated from Greek ēthos (meaning moral character) > ēthikos > ēthike > ēthike > Latin ethika > Old French etique (13th c.)> English Ethics (late 14c.).
Eulogy –
- Eulogise (v.) – To praise formally and eloquently.
- Eunice (n.) – Latinized form of Greek unikē meaning “victorious”. It comes from Eu meaning “good” with Nike, the Greek goddess of victory.
- Euphemism (n.) – the use of good words substituted for one that is considered offensive or too harsh. Syn. – genteelism, ant. – dysphemism. Formed by Eu “good, well” plus Greek Phēmē “prophetic speech, rumour or talk”.
- Euphoria – A state of intense happiness. Formed byEu “good, well” plus Greek phero meaning “to bear”.
Felinology –
- Faline (adj.) – Adjective for felis, “Cat-like”, of or pertaining to cat.
- Felicide (n.) – The killing of a cat. Formed by felis, “cat” plus Latin caedere “to kill or strike down”.
- Felinophobia (n.) – Fear of cats. Formed by felis plus phobos “fear, hatred, dislike”. Felinophobes are those people who dislike cats. The adjective is felinophobic.
Foetology/Fetology –
- Foeticide (n.) – The killing of the foetus. Formed by foetus, “unborn baby”, plus Latin caedere, “to kill”.
Formicology –
- Formicary (n.) – a mound of earth made by ants as they dig their nest.
- The adjective is formic. Formic acid (HCOOH) is an acid found in ants.
- Formication (n.) – crawling sensation as of an ant on the skin.
- Formicate (adj.) – crawling like an ant.
Gastrology or Gastroenterology –
- Gastric juices – Juices secreted from walls of the stomach.
- Gastronomy (n.) – The art of eating and preparing good food. Formed by gaster plus nomos (knowledge, rule, law).
-
- Gastrula (n.) – (Biology) Formed by gaster plus Latin -ula, a diminutive suffix. Literally means “little belly” or “little stomach”. Actually means the double-walled stage of the embryo (fertilised egg).
The adjective is gastrular; noun gastrulation.
- Gastropod (n.) – Formed by Greek gaster, “stomach”, plus Greek podos, “foot”. Literally refers to the feet from stomach (or, “stomach-foot”). Snails, slugs (shell-less snails), conches, limpets, sea hares etc. have muscular feet attached to their stomachs. See details.
- Gastrolith (n.) – It is a stone found in the stomach of various animals. The word is formed by Greek gaster meaning the “stomach” plus Greek lithos meaning “stone”.
Geochronology –
-
- Geocentrism (n.) – The description of the universe with the earth at the centre and the sun, moon, stars and other planets all orbit (move around) the Earth.
Formed by gē, “earth”, plus Greek kentron, “centre”.
- Geode (n.) – Geode literally means “earth-like” or “earthy”. It actually denotes a rounded stone with a hollow centre lined with crystals, identical to the shape of the earth. See images. Formed by gē “earth”, plus Greek suffix oidēs meaning “characterised by”.
Geology –
- Geography (n.) – Description of the earth’s surface. Formed by gē, “earth”, plus graphein “to describe”.
- Geographer is one who studies the earth’s surface.
Geomorphology –
- Morphology (n.) – Study of outer and inner structures of plant and animal bodies. Formed by morphē, “form, structure or shape”, plus logos, to study.
- Morphogeny – Biological developments of the forms of organisms (in Haeckel’s system). Formed by morphē, “form or shape”, plus Greek genes “born, produce”
- Morphogenesis (n.) – The production or shape of an organism. Formed by morphē, “form, shape”, plus genesis, “birth, origin or creation”.
Gerontology –
-
- Geriatrics (n.) – A branch of medical science that deals with the diseases and problem specific to old people. Formed by Greek geron “old man”, plus iatrikos, “healing”, from iatros, “a physician”.
Geriatrician is one who practises Gerontology or Geriatrics.
- Gerontocracy (n.)- Ruled by old people. The word is formed by Greek geron, plus kratia, “rule”. The adjective is gerontocratic.
Gynaecology –
- Gynaecolatry – Worship of women. Formed by Greek gyne, “woman”, plus latreia, “worship”.
- Gynarchy – Government by women. Formed by Greek gyne, plus arkhein, “to rule”.
- Misogyny – A feeling of hatred for women. Formed by Greek misein, “to hate”, or misos, “hatred”, plus Greek gyne, “woman”.
- Polygyny – A condition of having many wives at the same time. From Greek polys meaning “much” / “multi”. Plus gyne, “woman”. Opposite to polyandry (a condition of having many husbands at a time).
- Androgyny (n.) – A state of having traits of both masculine and feminine genders. Formed by Greek andros (genitive of anēr) “man”. Plus gyne, “woman”.The adjective is androgynous. An androgynous person or thing has the qualities of both men and women.
Nicknames like Pat, Sam, Chris are androgynous, because they are used by both men and women.
A synonym of androgyny is Hermaphroditism. The person is called Hermaphrodite. Let’s take a glance at the myth behind the formation of the word. - Gynaecomastia – Condition of a male having breasts like women’s, caused by a hormonal imbalance. The word is formed by Greek gyne, “woman”, plus Greek mastos, “women’s breast, mammary gland”.
Haematology –
- Haematophobia – Fear of blood. Formed by Greek haima, “blood”, plus phobos, “fear”.
- Haemophilia – Congenital tendency to uncontrolled bleeding. Formed by haima, “blood”, plus Philos, “love, friendship, tendency towards”. The adjective is haemophilic.
-
- Haemoglobin – A haemoprotein composed of haeme (a complex red organic pigment), and globin (a colourless protein) present in blood.
The word Haemoglobin is formed by Greek haima, plus globule, “a small spherical body; little globe” (denoting the shape of the protein globin).
- Haemorrhage – Bleeding violently from a ruptured blood vessel. Formed by Greek haima, “blood”, plus ragia (from rhegnunai) meaning “to break, burst”.
- Haemorrhoid – Vein, liable to discharge blood. Mainly referring to the venous swelling external or internal to the anal sphincter. (= Pile)
Heliology –
- Heliolatry – Worship of the sun. Formed by Helios, “the sun”, plus latreia, “to worship”.
-
- Heliocentrism – A model where the sun is at the centre of the universe, and the planets are revolving around it. The word is formed by helios, “the sun”, plus Greek kentron, “centre”.
Geocentrism, on the other hand, is a belief or a misbelief that the earth is at the centre of the universe, and the sun revolves around it.
-
- Heliotrope – A kind of plants that turn its flowers and leaves to the sun. Formed by Greek helios, plus trepein, “to run”.
- Heliograph – The description of the sun. Formed by helios, plus Greek graphein, “to describe”.
- Aphelion – The point on the elliptical orbit of a planet (or a comet or other astronomical objects) where it is the farthest from the sun. Formed by Greek prefix apo- meaning, “away” or “off” plus helios.
- Perihelion – The point on the elliptical orbit of a planet (or a comet or other astronomical objects) where it is the nearest to the sun. Formed by Greek prefix peri- meaning, “near” or “close” plus helios.
Hepatology –
- Hepatic (adj.) – related to the liver. Hepatic cells are the building blocks of the liver.
- Hepatic cirrhosis is a chronic disease interfering with the normal functioning of the liver.
- Hepatica is a type of plant. The word was derived from the same root, i.e. hepar, because its three-lobed leaves are thought to be identical to the human liver.
Herpetology –
-
- Herpes – Any viral disease. Its root lies in Greek herpes, meaning “creep”, as a viral disease spreads from one body to another as if by creeping.
Hippology –
- Hippocampus – A kind of sea monster, part horse and part fish. Formed by Greek hippos, “horse” plus kampos, “sea monster”. (Plural – hippocampi).
-
- Hippopotamus – . Formed by Greek hippos, “horse” plus potamos, “river”. Literally, “the horse of the river”.
The civilisation of Mesopotamia was between two rivers Tigris and Euphrates. Mesos means “middle” and potamos means “river”.
- Hippocrene (n.) – A fountain on Mount Helicon sacred to the muses, formed when the winged horse Pegasus struck its hoof into the ground. The waters were held to bestow poetic inspiration. Originates from Greek hippos plus krene, “fountain”.
- Hippodrome (n.) – Horse race course. In modern use, it is a circus performance place. In US slang, it is a fixed match or race. Formed by Greek hippos plus dromos, “course”.
- Hippomania (n.) – Excessive fondness for horses. Formed by Greek hippos plus Latin mania, “insanity or madness”.
- Hippophile (adj.) – One who loves horses. Formed by Greek hippos plus philein “to love”, or philos “loving”.
- Hippophagy – An act or practice of feeding on horse flesh (eating horses). Formed by Greek hippos plus phagous, “eating”.
Histology –
- Histamine (n.) – Amine (a chemical) found in some cells in the body. Histidine is another such amine.
Hydrology –
-
- Hydrogen (n.) – Hydrogen is a colourless gaseous element. The word is formed by Greek hydor “water” plus Greek -genes, “to produce”.
To hydrogenate is to cause to combine with hydrogen.
- Hydrogeology (n.) – It is the study of the distribution and movement of the ground water in the soil and the rocks of the earth’s crust. Formed by Greek hydor plus Geology meaning “the study of the earth”.
- Hydrography (n.) – The study of the measurement and description of the sea. Formed by Greek hydor plus graphein “to write, to describe”.
- Hydrolysis (n.) – Chemical composition by water. Formed by hydor plus Greek lysis “a loosening a dissolution”.
- Hydrometer (n.) – An instrument for measuring the specific gravity of a liquid or solid. Formed by hydor plus Greek metron “to measure”.
- Hydrophobia (n.) – Fear of water. formed by hydor plus Greek phobos “fear”. The adjective is hydrophobic.
Ichthyology –
- Ichthyomorhic (Adj.): Fish-shaped. formed by Greek ikhthus, combining with Greek morphe meaning “form, shape”.
- Ichthyophagous (n.): Fish eating. Formed by Greek ikhthus, combining with Greek phagein, meaning “to eat”.
-
- Ichthyosaur: A species of the marine reptiles of the Mesozoic period. Formed by Greek ikhthus, combining with Greek sauros, meaning “lizard”.
Sauros is the word forming element for dinosaur, tyrannosaurus etc.
Lepidopterology –
- Lepidoptera – The order of insects with four scaly wings.
Lithology –
- Lithodomous – A shellfish which lives in a hole of a rock. Formed by Greek lithos plus Greek demos meaning “house”.
- Lithograph – Printing from metal or stone surface.
- Litholatry – Worship of a rock. Formed by Greek lithos plus Greek latron, “worship/payment”.
- Idolatry is built on the same root. Greek eidolon meaning, “images”, plus Greek latron, “worship/payment”.
- Lithosphere – The outer part of the earth consisting of the crust and mantle. The word Lithosphere is formed by Greek lithos, plus Greek sphaira, meaning “Globe, ball, world”. So, etymologically lithosphere means the rocks of the globe.
- Lithotomy – Surgical removal of a stone. Formed by Greek lithos plus Greek tome, meaning “cutting”.
- Lithotripsy – The operation of crushing a calculus by using ultrasound. Formed by Greek lithos plus Greek teirein, “to rub, to rub away”.
Meteorology –
- Meteor – Any of the small solid extra terrestrial bodies that hits the earth’s atmosphere, built on the same root.
Microbiology –
Mycology –
- Mycosis – Presence of fungus as parasites in the body, causing a disease. Formed by Greek mykes plus -osis, meaning “a state of disease”.
Myology –
Myrmecology –
-
- Myrmecophily – Natural symbiosis with ants. Also refers to sharing the nest of ants.
The adjective is myrmecophilous. There are some myrmecophilous plants that attract ants to protect themselves from herbivores.
- Myrmecophagy – Ant eating. A feeding behaviour, defined by the consumption of termites or ants. The adjective is myrmecophagous. The myrmecophagous animals eat ants.
Nanotechnology, –
Neonatology –
Nephology –
- Nephophile – One who loves clouds. Formed by Greek nephos, plus Greek Philein, “to love”
Nephrology –
- Nephrolithiasis (n.) – The disease of formation of kidney stones. The word nephrolithiasis is formed by Greek nephros, plus lithos, meaning “stone” plus Greek suffix -asis, meaning “disease”.
- Nephrectomy – Surgical removal (excision) of a kidney. Formed by Greek nephron plus Greek ektomia, meaning “cutting out of”, from ektemnein, (ek, “out” ant temnein, “to cut”)
- Nephritis – Inflammation of the kidneys. Formed by Greek nephros, plus -itis meaning “inflammation”
- Nephridium – Sexual or renal organ of mollusks. The word is built on the same root nephros, “kidney”.
Neurology –
- Neuritis – Inflammation of the nerves. Formed by Greek neura, plus Greek itis meaning “inflammation”.
- Neuralgia – Acute pain across one or more nerves. Formed by neura plus Greek algos, meaning “pain”.
- Neuroglia – Connective tissue of the nerve centres. Formed by neura, plus Greek glia, meaning “glue”.
- Neuron – Nerve cell. A cell that is specialized to conduct nerve impulses. Built on the Greek root neura.
- Neurosis – A mental or personality disorder. Formed by neura, plus Greek -osis, meaning “a disease”.
Oceanology –
- Oceanography – The study of the physical and biological aspects of oceans (same as Oceanology). Formed by okeanos, plus Greek graphein, meaning “to write”.
-
- Oceania – A geographical area or a continent composed of many islands (Melanesia, Polynesia, Micronesia) along with Australia.
So named because the islands are connected with each other by the Pacific Ocean. And also,the land is connected with the other parts of the world by ocean.
Odonatology –
Odontology –
- Odontogenic (adj.) – of or pertaining to the origin and development of the teeth. Formed by odous plus Greek genes, meaning “origin, offspring or kind”, from Proto-Indo-European root -gen, meaning “to give birth to”.
Oncology –
- Oncogenesis – Formation of tumors. The word oncogenesis comes from ogkos plus Greek genes, from Proto-Indo-European root -gen, meaning “to give birth to”.
- Oncogene is gene that disposes normal cells to transform into cancerous tumor cells.
Oology –
- Oocyte – a female gametocyte that develops into an ovum after two meiotic divisions. Comes from oon, plus Greek kytos, meaning “a hollow basket, vessel or jar that resembles a cell”.
- Oogenesis – The formation and development of the ovum. The word oogenesis comes from oon, plus Greek genes, from Proto-Indo-European root -gen, meaning “to give birth to”.
- Oolite – A sedimentary rock formed from spherical grains. Oolite comes from oon, plus Greek lithos, “stone”. See images of oolite.
Ophiology –
- Ophiophile – One who loves snakes. From Greek ophis, “snake”, plus philein, “to love”.
- Ophiophage – One who eats snakes. From Greek ophis, “snake”, plus phagein, “to eat”.
- Ophiolatry – Worshipping snakes. From Greek ophis, plus latreia, “worship”.
The word idolatry means “worshipping idols”. Formed by Greek eidolon, “image, idol”, plus latreia, “worship”.
- Ophisaurus – A kind of lizard resembling a snake. From Greek ophis, “snake”, plus sauros, “lizard”. They are also known as glass lizard, glass snakes etc. See images of ophisaurus.
- Ophioglossum – It is a kind of plant, the fertile part of which resembles the tongue of a snake. From Greek ophis, “snake”, plus glossa, “tongue”.
- Ophiolite is a stone, the texture of which resembles that of a snakeskin. Formed by Greek ophis, plus lithos, “stone”. See images.
Ophthalmology –
- Ophthalmia – Swelling of the eye or conjunctivitis. Formed by ophthalmos, plus -ia. the element -ia is used to name countries, diseases and flowers.
- Ophthalmoscope – An instrument to examine the retina of the eye. Formed by ophthalmos, plus Greek skopein, “to see, observe, examine”.
Ornithology –
- Ornithomancy – Divination by means of birds. Formed by ornithos plus Greek manteia, “oracle, divination”.
- Ornithopod – The species of dinosaurs whose hind legs were like those of birds. The word is formed by ornithos, plus Greek podos, “foot”.
- Ornithopter – A machine designed to fly by mechanical flapping of wings. Formed by ornithos, plus Greek pteron, “wing”.
- Pteron is the root of the word helicopter also. “Helicopter” is built on helikos, “spiral”, + pteron. The idea was to gain lift from spiral aerolift.
Orology –
- Orography – Study or description of the mountains (having the same meaning as orology.)
- Orographic Rainfall – Orographic Rainfall is a type of precipitation that occurs when moist air rises over a mountain.
Orthopterology –
- Orthodontics – The branch of dentistry dealing with the prevention or correction of the irregularities of the teeth and the jaw, or making the teeth straight. Formed by orthos, “straight” plus Greek odous, “teeth”.
- Orthognathous – Straight-jawed; jaw not projecting beyond the vertical line of the forehead. Formed by Greek gnathos meaning, “jaw”.
- Orthography – The art of writing words with the proper letters according to the standard usage. Formed by orthos, “straight, correct”, plus graphein, “to write”.
- Orthopaedics – The branch of science concerned with the disorder or deformities of the spine and joints specially in children. Formed by orthos, “straight”, plus Greek paidos, “children”.An orthopedist is one who deals with the natural deformities in the human body.
- Orthopraxy – Correct practice or procedure for a specific purpose. Formed by orthos, “correct” plus Greek praxis, “to do, to act”.
Osteology –
- Osteopathy – Disease of the bones. The word is formed by osteon, “bone”, plus Greek pathos, “disease, suffering, feeling”.
- Osteoporosis – Abnormal loss of bony tissue resulting in fragile porous bones. Formed by osteos, “bone”, plus Greek poros, “passes; pore; voyage”.
Otology –
- Otocrane – The cavity in the skull in which the parts of the internal ear in located. the word is formed by ous “ear”, plus Greek kranion, “skull”.
- Otocyst – An organ involved in balance and orientation. Formed by Latin cysts, from Greek kustis, “anatomical sac”.
Parasitology –
Pathology –
- Pathogen – Producing diseases. Formed by pathos, “disease; suffering”; plus genos, “birth”. Pathogenesis means the origination and development of a disease. Pathogenic is the adjective.
- Pathognomonic – Spacially or decisively a characteristic of a disease. Formed by pathos, ” plus gnomonikos, “fit to judge of”.
- Pathophysiology – The changes in function as a result of disease or injury. Formed by pathos, “disease; suffering”, plus Greek physios, “nature”, plus Greek logos, “study”.
Petrology –
- Petroleum – An oily substance obtained from certain rock beds. The word petroleum is formed by Latin petra, “rock”, plus oleum, “oil”.
- Petrochemical (n.) – Chemical products obtained from petroleum or natural gas by refining.
- Petrochemical (adj.) – Of or pertaining to the chemistry of the formation of rocks.
- Petrodollar – Money earned by export sales of petroleum products.
- Petroglyph – A carving or line drawing on rock. Formed by petros, “rock”, plus glyphe, “carving”.
Pharmacology –
Phonology –
- Phoneme – One of a small set of speech sound. Formed by Greek phone. The adjective is Phonemic.
- Phonetics – Study of speech (also phonics). Formed by Greek phonetikos, “vocal”. The adjective is phonetic.
- Phonogram – Any written symbol for a sound, syllable or a word. Formed by Greek gramma, “A picture, a drawing, a character, an alphabet,”; from the stem graphein, “to write, draw”.
- Phonograph – Characters representing sounds. From phone, “sound”, + Greek graphein, “to write”.
- Phonolite – Literally “sounding stone” A kind of rock that rings when struck. From phone, “sound” + Greek lithos, “stone”
- Phonomania – Irresistible desire to murder (oneself or other). From Greek phonos, “murder” + mania, “madness, frenzy”.
- Phonophobia – Fear of loud sounds. From phone, “sound” + fobia, “fear”.
- Cacophony – A harsh discordant mixture of sounds. Formed by Greek kakos, meaning “bad”.
- Euphony – The quality of being pleasing to the ear. Formed by Greek eu, “well”.
- Polyphony – Simultaneously combining a number of musical parts in harmony. Formed by Greek polloi, “many”.
Phycology –
Physiology –
- Physiognomy – The art of judging people by their facial expression. From physios, “nature”, + Proto-Indo-European gno-, “to know”.
- Physiotherapy – Treatment of disease by physical method. Formed by Greek physios, “body”, + Latin thrapia, meaning “healing, curing”, from Greek therapeuein, “to heal, cure”.
Phytology –
- Phytoplankton – Plant constituent of plankton, mainly unicellular algae. Planktons are the organism that lives in a large body of water and is unable to swim against the current. The word is formed by Greek phyton, “plant”; + Greek plankton, “wandering, drifting”.
- Bryophyte – Group of plants comprising mosses and liverworts. From Greek bryos, “moss” + phyton, “plant”.
- Thallophyte – A group of plant-like organisms that lack distinguished leaves, stems, or roots. From Greek thallos, “young shoot or twig”, plus phyton, “plant”.
- Xerophyte – Plants that grow where there is limited supply of water. Greek xeros, “dry” + phyton, “plant”, literally, plants that grow in arid (dry) climate.
- Chrysophyte – Chrysophyte is a kind of golden algae. From Greek khrusos, “gold” + phyton, “plant”.
- Gametophyte – A plant (or the haploid phase in its life cycle) that produces gametes by mitosis to produce a zygote. From Greek gamete, “wife” and gametes, “husband” + phyton, “plant”.*This gamete or gametes comes from Greek gamos, meaning “marriage”, being the root of monogamy, bigamy, polygamy, misogamy.
- Monogamy – The practice or the state of having one spouse at a time. Greek monos, “single or one”, + gamos, “marriage”.
- Bigamy – The statement of having two spouses at the same time. From Proto-Indo-European root dwo, “two” > old Latin dvi, (cognate in Sanskrit dwi) > Greek di, dis.
- Polygamy – The state of having more than one spouse at the same time. From Greek polys, “many” + gamos, “marriage”.
- Polygyny – Having many wives at the same time. From polys, “many” + gune, “woman”.
- Polyandry – Having many husbands at the same time. From Greek andr-, from Proto-Indo-European aner, “man”.
- Polygynandry – Its a combination of polygyny + polyandry, which refers to a mating pattern of multiple males and multiple females.
- Androgyne is one who has the qualities of both male and female. Hermaphrodite is another term for him/her.
- Misogyny – A hatred of women. From Greek misein, “to hate” + gune, “woman”.
- Misandry – A hatred of men. From Greek misein, “to hate” + aner, “man”.
- Hydrophyte – Seaweed; plants that grow under the sea water. From Greek hudor, “water” + phyton,”plant”.
- Zoophyte – A kind of animals resembling a plant such as sea anemone, coral or sponge. From Greek zoion, “animal” + phyton, “plant”. See images of zoophytes.
- Cycadophyte – Palm-like gymnosperms. From Greek kykas, from Theophrastus’ koikas, “palm trees”.
- Hygrophyte – A plant that grows in a moist area. From Greek hygros, “wet” + phyton, “plant”.
- Xerophyte – Plants that grow in dry areas. From Greek xeros, “dry”, + phyton, “plant”.
- Gametophyte – A sexual phase in the life cycle of a plant or an algae. From Greek gamete, “wife”, + phyton,”plant”.
- Chamaephyte – Any herbaceous or woody plants whose buds overwinter just above the soil level.
Phytopathology –
Planetology –
Planktology –
- Zooplankton – Animals that live in a large body of water and swim along the current. Comes from Greek zoion, “animal”, plus plankton.
- Phytoplankton – Plants that live in a large body of water and swim along the current. Comes from Greek phyton, “plant”, plus plankton.
Pomology –
- Pomiculture – Cultivation of fruits. Formed by Latin pomum, “fruit”, plus cultura, “cultivate”.
- Pomegranate – A type of fruit with many seeds. Comes from Latin pomum, “fruit/apple” + granatum, “having many seeds”. Pomegranate literally means, “An apple with many seeds”. See images of pomegranates.
Primatology –
- Prime – First in rank or degree. From primus, “first”.
- Primacy – Supremacy. From primus, “first”.
- Primal – Having existed from the beginning. From primus, “first”.
- Prima facie – As it seems at first sight; clear. Formed by Latin primus, “first”, plus facies, “face, appearance, form”. In law the phrase Prima facie describes a fact or presumption that is sufficient to be regarded as true unless otherwise proved or rebutted.
- Prima donna – First lady; or the leading female singer in an opera. Formed by Latin prima, (feminine of primus), “first”, plus domina, “lady”.
- Prima ballerina – The leading ballet dancer.
- Primogenitor – An ancestor in the direct line. Formed by primus, “first”, plus genitor, “father”.
Psychology –
- Psychokinesis – The psychic power to move objects. Formed by psykhe, plus Greek kinein, “to move”.
- Psychomancy – Communication between souls or with spirits. Formed by Greek psykhe, plus manteia, “oracle, divination”.
- Psychometry – Measuring of the mind – The science of measuring mental capacities. From Greek psykhe, plus metron, “to measure”.
- Psychopath – One who is suffering from a mental illness; a morally irresponsible person. From Greek psykhe, plus pathos, “suffering”.
- Psychosomatic – The word is used for illness or symptoms resulting from neurosis. A psychosomatic disease is bodily disease caused by some intense unwillingness to do something. Formed by Greek psykhe, plus somatos, “body”.
- Psychotropic (adj.) – Something that affects a person’s mental state. From Greek psykhe, plus trepein, “to turn”. A psychotropic drug affects the mental states. A psychotic person is one who is suffering form psychosis or mental illness.
Pulmonology –
Radiology –
- Radio – Wireless transmission of radio waves. From Latin radius, “beam”, as the wireless signals are transmitted through waves or beams of rays.
- Radioactive – Exhibiting radioactivity. Radioactivity is the spontaneous emission of a stream of particles. From Latin radius, “ray”, plus actif, “Active”.
- Radio-carbon – The radio carbon or carbon-14 is the radio-active isotope of carbon. This isotope (C-14) is used in radio-carbon dating to determine the age of organic materials. An American chemist Willard Libby discovered this method in 1940.
-
- Radiography – The process of forming images on a sensitive plate by means of radiation (X-rays).
The discovery of X-rays by German physicist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen in 1895 originated the term radiography. Röntgen noticed that X-rays could pass through human tissue but not through bones or metals. He named the ray “X” as it was of an unknown type. Röntgen took the first X-ray photograph of his wife’s hand.
- Radiolarian – A kind of amoeboid protist with spines. From Latin radiolus (small sun beams), diminutive of radius. The skeletons of radiolarians are generally organized around spicules, or spines, which extend from the main skeletal mass.
- Radiometric – Adjective of radiometer. A radiometer is an instrument that measures the intensity of a radiant energy.
- Radioscopy – Examination by means of X-rays. Formed by Latin radius, plus scopium, “to look at; examine”
- Radiotherapy – The therapy using the radiation. From Greek radius, plus Greek therapeia, “curing”.
- Radiocast – This word is used for radio broadcast.
Rhinology –
- Rhinoplasty is the plastic surgery of the nose.
- Rhinorrhea – Continuous watery mucous discharge from the nose. Formed by Greek rhinos, “nose”, plus rhoia, meaning “flow”.
- Rhinoceros – A kind of beast with a horn on its nose. From Greek rhinos, “nose”, plus ceros, from keros,”horn”.
- Platyrrhine monkeys are a type of monkeys that have a flat nose, the nostrils are wide apart. From Greek platus, “flat”, plus rhinos, “nose”.
- Catarrhine monkeys have nostrils that face downward. From Greek kata, “down”, plus rhinos, “nose”.
Saurology –
- Sauromalus – Chuckwallas; a kind of herbivorous lizard. Formed by Greek sauros, “lizard”, plus omalus, “flat”.
- Dinosaur – The Mesozoic reptile of enormous size. From Greek dinos, “terrible”, plus sorous, “lizard”
- Tyrannosaurus Rex or T. rex is the largest species of dinosaur discovered so far. From Greek tyrannos, “tyrant”, plus sauros, “lizard”, plus rex, “king”; etymologically, “a tyrant king”.
Seismology –
- Seismograph – An instrument to measure the intensity, direction and duration of an earthquake. From seismos, “earthquake”, plus graphein, “to write, to measure”.
- Seismogram – The record made by a seismograph. From Greek seismos, “earthquake”, plus gramma, “drawing, picture”.
Selenology –
- Selenographer is one who studies the physiography of the moon.
- Selenotropism is growth in response to the moonlight. From Greek selene, ” moon”, plus tropos, “a turning/a growth”
Sociobiology –
Sociology –
- Sociopath – One who has an anti social behaviour or mental attitude. From Greek socius, “society”, plus pathos, “suffering”.
Somatology –
- Somatic cells (which are not the egg of sperm cells,) are building blocks of a body.
- A psychosomatic disease is a bodily disease caused by a particular state of our psyche, “mind” such as intense unwillingness to do something that is compulsory.
Somnology –
- Somnambulism – The act or habit of walking while asleep. From Latin somnus, “sleep”, plus ambulare “to walk”.
- Somniloquy – The habit of talking while asleep. From Latin somnus, “sleep” plus loqui, “to speak”.
- Somniferous – Sleep-inducing; soporific; something that induces sleep. From Latin somnus, “sleep”, plus ferre, “to carry to bear.
- Somnolescent – Sleepy, drowsy, lethargic.
- Somnolence – Sleepiness, drowsiness. Adjective – somnolent.
Speleology –
- Speleogenesis is the study of the origin and development of caves. From Greek spelaion, “cave”, plus Greek genesis, “origin, source, beginning”.
- Speleomorphology is the study of the change of caves over time.
- Speleomantes are the European cave salamanders. From Greek spelaion, “cave”, plus Greek mantes, “oracle, seer, prophet”. The name “Speleomantes” therefore suggests “cave oracle” or “seer of the cave”, which is a fitting name for a genus of salamanders that live in caves and other subterranean habitats.
Stomatology –
- The word stomach is built on the same root.
Technology –
- Technetium – An element artificially created.
- Technocracy – A society or a government controlled by technical experts. From Greek tekhne, “art, craft, skill”, plus kratia, “power, rule, might”.
- Technophile – Who love technology. From Greek tekhne, “skill, craft”, plus philein, “to love”
- Technophobe – Who fear or hate technology. From Greek tekhne, “skill, craft”, plus phobos, “fear, hatred”.
Thermology –
- Thermal and thermic are the adjectives of temperature.
- Thermochemistry is the subject that studies the relation between the chemical actions and heat.
- Thermocline – A layer in a body of water with a temperature gradient separating surface water from cooler lower water.” From Greek thermos, plus klinein “to slope”
- Thermodynamics – The study of the relationships between heat, work, and the energy content of a system at equilibrium. From thermos, plus dynamikos, “force, power”.
- Thermoelectric – The thermoelectric effect is the direct conversion of temperature differences to electric voltage and vice versa via a thermocouple.
- Thermography – A technique that uses infrared cameras to create images that show how heat is distributed across the surface of an object. From Greek thermos, plus graphein “to write”.
- Thermometer – The instrument that is used to measure temperature of a solid, liquid or a gas. From Greek thermos, plus metron, “measure”.
Tocology –
- Tocopherol – Chemical name of vitamin E. From Greek tokos, “childbirth”, plus pherein, “to bear, to carry”, plus -ol, suffix used for alcohol. So named because vitamin E or tocopherol is essential in fertilized eggs for live birth.
Topology –
- Topography – Description of the surface features of a geographical location. From Greek topos, “place”, plus graphein, “to describe, to write”.
- Toponym – The name of a geographical location. From Greek topos, “place, location”, plus onoma or no-men, “name”.
Trichology –
Virology –
- Virologist is one who studies virology.
Volcanology –
Xylology –
- Xylem, built in the same root xúlon, is the primary component of wood. Xylem is the tissue responsible for the distribution of water and minerals taken up by the roots.
- Protoxylem – Protoxylem is the primary xylem that develops first during primary growth. From Greek protos, “first”, superlative of pro, “before”.
- Metaxylem – Metaxylem is a part of the primary xylem in plants that matures after the protoxylem. From Greek meta, “last, middle”, plus xúlon, “wood”.
Zoology –
- Zodiac – The zodiac signs are a belt that extends on either side of the ecliptic plane, which is the path of the sun and the Earth’s orbit. The zodiac signs include some pictures of animals. From Greek zoion, “animal”.
- Zooplankton are the animals that live in a large body of water and swim along the current. From Greek zoion, “animal”, plus plankton.
Zymology –
- Zymozen – An inactive protein precursor of an enzyme secreted by living cells and converted (as by a kinase or an acid) into an active form. called also proenzyme. From Greek zúmē, “leaven”, plus genes, “producer, agent”.