What is Voice?
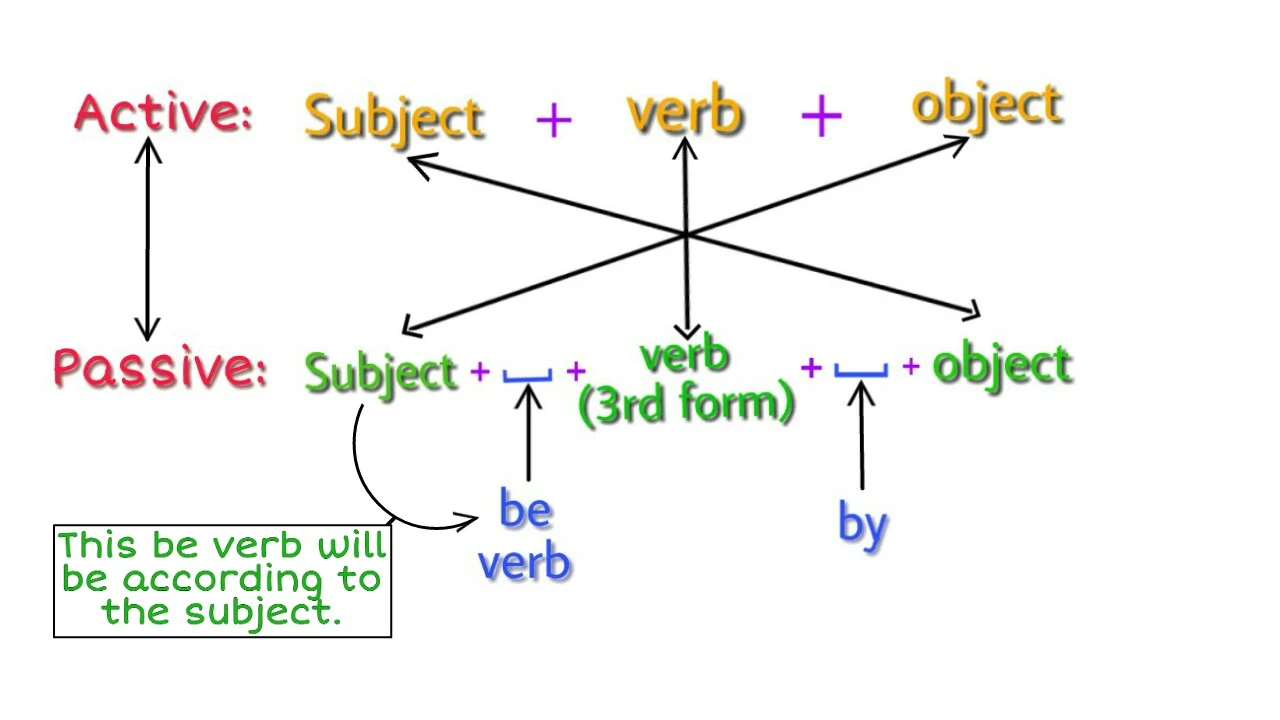
Voice is the form of a verb which indicates whether the subject does the work (active) or something is done to the subject (passive).Voice can be classified as –
- Tom writes a letter.
- We read books.
- She teaches us.
So, these sentences are in active voice.
Again, without changing the meaning if we write those sentences as –
- A letter is written by Tom.
- Books are read by us.
- We are taught by her.
Then, we see, the subjects ('A letter', 'Books', 'We') do not do anything, rather something is done to them by someone.
So, we can say, the subjects are passive and the sentences are in passive voice.
Hence, voice is of two types –
i) Active Voice, and
ii) Passive Voice.
In exams we are asked to change the voice of a sentence from active to passive or from passive to active. So let's learn how to change the voice of a sentence along with sentence-structures –
- The object of active voice becomes the subject in passive voice.
- This subject of passive is followed by a be verb (according to the subject). [Subject + be verb]
- The be verb is followed by the 3rd form of the main verb. [subject + be verb + M.V.3]
- The subject of the active voice becomes the object of the passive voice and a 'by' is used before this object. [Subject + be verb + M.V.3 + by + object]
A personal pronoun has two forms— a subjective form and an objective form. If the subject of the active voice is a personal pronoun, it is changed to its objective form when it becomes object in the passive and vice versa. Like,
Active –They invite us.
Passive – We are invited by them.
–Subject ‘They’ becomes object ‘them’.
Object ‘us’ becomes subject ‘We’.
● List of Subjective Case and objective Case of personal pronouns :–
| Subjective Case | Objective Case |
|---|---|
| I (I do...) | me (...by me) |
| We (We do...) | us (...by us) |
| You (You do...) | you (...by you) |
| He (He does...) | him (...by him) |
| She (she does...) | her (...by her) |
| They (They do...) | them (...by them) |
Also read: Pronoun.
Also read: Noun and the Case.
Changing the voice of an—
Example:
Active – We play football.
Passive – Football is played by us.
Structure for negative:
Example-Rules to change the voice in sentence-wise:
We already know that there are five types of sentence (Assertive, Imperative, Interrogative etc.).
Changing the voice of an—
Assertive Sentence:
Structure:
Active – Subject + verb + object.
Passive – Subject (object of the active) + be verb + 3rd form of the main verb + by + Object (subject of the active).
Passive – Subject (object of the active) + be verb + 3rd form of the main verb + by + Object (subject of the active).
Example:
Active – We play football.
Passive – Football is played by us.
Structure for negative:
Active – Subject + do/does + not + verb + object.
Passive – Subject (object of the active) + be verb + not + 3rd form of the main verb + by + Object (subject of the active).
Passive – Subject (object of the active) + be verb + not + 3rd form of the main verb + by + Object (subject of the active).
Active – She does not love movies.
Passive – Movies are not loved by her.
Interrogative Sentence:
Interrogative sentence are classified as—i) Yes-No Questions,
ii) WH Questions.
i) Yes-No Questions-
The answer to a question of this sort is either ‘Yes’ or ‘No’.Structure:
Active – Do verb + subject + verb + object + ?.
Passive – Be verb + passive subject + V3 + by + passive object + ?.
Examples-Passive – Be verb + passive subject + V3 + by + passive object + ?.
Active – Do you play football?
Passive – Is football played by you?
Active – Doesn’t she teach you English?
Passive – Aren’t you taught English by her? Or, Isn’t English taught to you by her?
Active – Did he play cricket?
Passive – Was cricket played by him.
Active – Did you received my letter in time?
Passive – Was my letter received in time by you?
Passive – Was my letter received in time by you?
Read more: Framing Questions - Yes-No and WH Questions.
ii) WH Questions-
These questions begin with Wh-words (what, who, whom, when etc.)Structure:
Active – Wh + do verb + subject + main verb + object + ?.
Passive – Wh + be verb + passive subject + main verb (3rd form) + by + passive object + ?.
Passive – Wh + be verb + passive subject + main verb (3rd form) + by + passive object + ?.
Examples-
Active – When do you eat your breakfast?
Passive – When is your breakfast eaten by you?
Active – Why don’t you pay the money?
Passive – Why isn’t the money paid by you?
Active – Where did Darren keep the box?
Passive – Where was the box kept by Darren?
Active – How will he do that?
Passive – How will that be done by him?
Rules for What, How many and How much.
Here the sentences are without object.
Structure:
Active – What + helping verb + subject + main verb + ?.
Passive – What + be verb + 3rd form of the main verb + by + passive object + ?.
Passive – What + be verb + 3rd form of the main verb + by + passive object + ?.
Examples-
Active – What do you see?
Passive – What is seen by you?
Active – What does he buy?
Passive – What is bought by him?
Structure:
Active – How many / How much + noun + helping verb + subject + main verb (3rd form) + ?.
Passive – How many / How much + noun + be verb + main verb (3rd form) + by + passive object + ?.
Passive – How many / How much + noun + be verb + main verb (3rd form) + by + passive object + ?.
Active – How many books do you read?
Passive – How many books are read by you?
Active – How much water do you drink?
Passive – How much water is drunk by you?
An interrogative sentence may not have a do-verb or any other helping verb. When an Interrogative sentence starts with What without a do verb –
then the structure will be:
Active – What + verb + object + ?
Passive – By + what + be verb + subject + main verb (3rd form) + ?.
Passive – By + what + be verb + subject + main verb (3rd form) + ?.
Examples-
Active – What helps you to come back?
Passive – By what are you helped to come back?
Active – What causes cancer?
Passive – By what is cancer caused?
Imperative Sentence:
There are three types of imperative sentence — order, request and advice.If the imperative sentence expresses an order—
Change the voice using ‘Let’:
Structure:
Active – Verb + object.
Passive – Let + subject (object of active) + be + V3.
Passive – Let + subject (object of active) + be + V3.
Example-
Active – Close the window.
Passive – Let the window be closed.
put a not after the let when the active is a negative-
Active – Don't make a noise.
Passive – Let not a noise be made.
If the imperative sentence expresses an advice —
Structure:
Active – Verb + object.
Passive 1 – Object + should be + verb (3rd form) Use should+not for negative.
Passive 2 – You are + advised to + verb + object*.
Passive 1 – Object + should be + verb (3rd form) Use should+not for negative.
Passive 2 – You are + advised to + verb + object*.
*Remember, here in the passive form, the object is the same object of the active and not the subject of the same.
Examples-
Active – Respect your elders.
Passive 1 – Your elders should be respected.
Passive 2 – You are advised to respect your elders.
For a negative sentence-
Active – Don't insult the poor.
Passive 1 – The poor should not be insulted.
Passive 2 – You are advised not to insult the poor.
If the imperative sentence denotes a request—
Structure:
*Omit Please/Kindly in the passive.
Examples-
Active – Please give me a glass of water.
Passive – You are requested to give me a glass of water.
Active – Kindly check my notes.
Passive – You are requested to check my notes.
Example-
Active – May you win the match.
Passive – May the match be won by you.
Active – May he pass the exam.
Passive – May the exam be passed by him.
The most important thing we have to remember is that-
Every helping verb of the passive will be according to its subject.
Like-
Active – We have done this.
Passive – This has* been done by us.
* Here in the active voice, 'We' is a plural subject, so it is followed by a plural have verb have.
But on the other hand, in the passive voice, the subject 'This' is a singular subject, so it is followed by a singular have verb - has.
Examples:
Active – Kishan visits the zoo.
Passive – The zoo is visited by Kishan.
Active – We do not drink water.
Passive – Water is not drunk by us.
Active – Do they know you?
Passive – Are you known to them?
*being is used because of the ing form of the main verb.
Examples-
Active – I am speaking English.
Passive – English is being spoken by us.
Active – She is writing a letter.
Passive – A letter is being written by her.
Active – He is not following the rules.
Passive – The rules are not being followed by him.
Active – Is she drawing a picture?
Passive – Is a picture being drawn by her?
*been acts as a be verb itself. It is the 3rd form of 'be'.
Examples-
Active – We have drunk water.
Passive – Water has been drunk by us.
Active – The club has not organised the show.
Passive – The show has not been organised by the club.
Active – Has they scored a goal?
Passive – Has a goal been scored by them?
Examples-
Active – We drank water.
Passive – Water was drank by us.
Active – I did not call them.
Passive – They were not called by me.
Active – Did I make a mistake?
Passive – Was a mistake made by me?
Examples-
Active – He was eating rice.
Passive – Rice was being eaten by him.
Active – They were not opening the gate.
Passive – The gate was not being opened by them.
Active – Were you driving the car?
Passive – Was the car being driven by you?
Examples-
Active – John had gone to school.
Passive – School had been gone to by John.
Active – We had not solved the matter.
Passive – The matter had not been solved by us.
Active – Had the girl bought the chocolates.
Passive – Had the chocolates been bought by the girl?
Active – Respect your elders.
Passive 1 – Your elders should be respected.
Passive 2 – You are advised to respect your elders.
For a negative sentence-
Active – Don't insult the poor.
Passive 1 – The poor should not be insulted.
Passive 2 – You are advised not to insult the poor.
If the imperative sentence denotes a request—
Structure:
Active – Please/Kindly* + verb + object.
Passive – You are requested to + verb + object (object of active).
Passive – You are requested to + verb + object (object of active).
*Omit Please/Kindly in the passive.
Examples-
Active – Please give me a glass of water.
Passive – You are requested to give me a glass of water.
Active – Kindly check my notes.
Passive – You are requested to check my notes.
Optative Sentence:
Structure:
Active – May + subject + verb + object.
Passive – May + passive subject + be + V3 + by + passive object.
Passive – May + passive subject + be + V3 + by + passive object.
Example-
Active – May you win the match.
Passive – May the match be won by you.
Active – May he pass the exam.
Passive – May the exam be passed by him.
Rules to Change the Voice - In Tense-wise
The most important thing we have to remember is that-
Every helping verb of the passive will be according to its subject.
Like-
Active – We have done this.
Passive – This has* been done by us.
* Here in the active voice, 'We' is a plural subject, so it is followed by a plural have verb have.
But on the other hand, in the passive voice, the subject 'This' is a singular subject, so it is followed by a singular have verb - has.
Present Indefinite Tense :-
Structure:
Active – Subject + verb + object.
Passive – Subject (object of the active voice) + am/is/are + main verb (3rd form) + by + object (subject of the passive voice).
Passive – Subject (object of the active voice) + am/is/are + main verb (3rd form) + by + object (subject of the passive voice).
Examples:
Active – Kishan visits the zoo.
Passive – The zoo is visited by Kishan.
Active – We do not drink water.
Passive – Water is not drunk by us.
Active – Do they know you?
Passive – Are you known to them?
Present Continuous Tense :-
Structure:
Active – Subject + am/is/are + (verb+ing) + object.
Passive – Subject + am/is/are + being* + main verb (3rd form) + by + object.
Passive – Subject + am/is/are + being* + main verb (3rd form) + by + object.
*being is used because of the ing form of the main verb.
Examples-
Active – I am speaking English.
Passive – English is being spoken by us.
Active – She is writing a letter.
Passive – A letter is being written by her.
Active – He is not following the rules.
Passive – The rules are not being followed by him.
Active – Is she drawing a picture?
Passive – Is a picture being drawn by her?
Present Perfect Tense :-
Structure:
Active – Subject + have/has + main verb (3rd form) + object.
Passive – Subject + have/has + been* + main verb (3rd form) + by + object.
Passive – Subject + have/has + been* + main verb (3rd form) + by + object.
*been acts as a be verb itself. It is the 3rd form of 'be'.
Examples-
Active – We have drunk water.
Passive – Water has been drunk by us.
Active – The club has not organised the show.
Passive – The show has not been organised by the club.
Active – Has they scored a goal?
Passive – Has a goal been scored by them?
Present Perfect Continuous Tense :-
Structure:
Active – Subject + have/has + been + main verb+ing + object +...
Passive – Subject + have/has + been* + being + main verb (3rd form) + by + object + ...
Passive – Subject + have/has + been* + being + main verb (3rd form) + by + object + ...
Examples-
Active – We have been playing football for an hour.
Passive – Football has been being played for an hour by us.
Active – We have been playing football for an hour.
Passive – Football has been being played for an hour by us.
Active – Has the teacher been teaching us for fifty minutes?
Passive – Have we been being taught by the teacher for fifty minutes?
Passive – Have we been being taught by the teacher for fifty minutes?
Active – Have not I been teaching you for two hours?
Passive – Have not you been being taught by me for two hours?
Passive – Have not you been being taught by me for two hours?
Past Indefinite Tense :-
Structure:
Active – Subject + Past form of verb (V2) + object.
Passive – Subject (object of the active) + was/were + main verb (3rd form) + by + object (subject of the active).
Passive – Subject (object of the active) + was/were + main verb (3rd form) + by + object (subject of the active).
Examples-
Active – We drank water.
Passive – Water was drank by us.
Active – I did not call them.
Passive – They were not called by me.
Active – Did I make a mistake?
Passive – Was a mistake made by me?
Past Continuous Tense:-
Structure:
Active – Subject + was/were + (verb+ing) + object.
Passive – Subject + was/were + being + V3 + by + object.
Passive – Subject + was/were + being + V3 + by + object.
Examples-
Active – He was eating rice.
Passive – Rice was being eaten by him.
Active – They were not opening the gate.
Passive – The gate was not being opened by them.
Active – Were you driving the car?
Passive – Was the car being driven by you?
Past Perfect Tense :-
Structure:
Active – Subject + had + main verb (3rd form) + object.
Passive – Subject + had + been + V3 + by + object.
Passive – Subject + had + been + V3 + by + object.
Examples-
Active – John had gone to school.
Passive – School had been gone to by John.
Active – We had not solved the matter.
Passive – The matter had not been solved by us.
Active – Had the girl bought the chocolates.
Passive – Had the chocolates been bought by the girl?
Past Perfect Continuous Tense :-
Structure:
Active – Subject + had + been + main verb+ing + object +...
Passive – Subject + have/has + been* + being + main verb (3rd form) + by + object + ...
Passive – Subject + have/has + been* + being + main verb (3rd form) + by + object + ...
Examples-
Active – We had been playing football for an hour.
Passive – Football had been being played for an hour by us.
Active – We had been playing football for an hour.
Passive – Football had been being played for an hour by us.
Active – Had the teacher been teaching us for fifty minutes?
Passive – Had we been being taught by the teacher for fifty minutes?
Passive – Had we been being taught by the teacher for fifty minutes?
Active – Had not I been teaching you for two hours?
Passive – Had not you been being taught by me for two hours?
Passive – Had not you been being taught by me for two hours?
Read more: Past tense.
Future Indefinite Tense:-
Structure:
Active – Subject + shall/will + verb + object.
Passive – Subject + shall/will + be + main verb (3rd form) + by + object.
Passive – Subject + shall/will + be + main verb (3rd form) + by + object.
Examples-
Active – I shall drink water.
Passive – Water will be drunk by me.
Active – Sissy will not do the work.
Passive – The work will not be completed by Sissy.
Active – Shall we buy some apples?
Passive – Will some apples be bought by us?
Future Continuous Tense:-
Structure:
Active – Subject + shall/will + be + (verb+ing) + object.
Passive – Subject + shall/will + be + being + V3 + by + object.
Passive – Subject + shall/will + be + being + V3 + by + object.
Examples-
Active – I shall be eating rice.
Passive – Rice shall be being eaten by me.
Active – They will not be forcing you.
Passive – You will not be being forced by them.
Active – Will she play cricket?
Passive – Will cricket be being played by her?
Future Perfect Tense :-
Structure:Active – Subject + shall/will + have + main verb (3rd form) + object.
Passive – Subject + shall/will + have + been* + main verb (3rd form) + by + object.
*been acts as a be verb itself. It is the 3rd form of 'be'.
Examples-
Active – We shall have drunk water.
Passive – Water will have been drunk by us.
Active – The club will not have organised the show.
Passive – The show will not have been organised by the club.
Read more: Future tense.
Change the voice of a sentence with Modal Auxiliary Verbs –
Structure:
Active – Subject + modal verb + main verb + object.
Passive – Subject + modal verb + be + main verb (3rd form) + by + object.
Passive – Subject + modal verb + be + main verb (3rd form) + by + object.
Example-
Active – I can do it.
Passive – It can be done by me.
Active – You may not find some errors.
Passive – Some errors may not be found by you.
Active – She will not drive the car.
Passive – The car will not be driven by her.
Active – The man would say something.
Passive – Something would be said by the man.
Active – She should accept the proposal.
Passive – The proposal should be accepted by her.
Active – Rocky must attend the seminar.
Passive – The seminar must be attended by Rocky.
Interrogative with Modal Verbs:
Structure:
Active – Modal auxiliary verb + subject + main verb + object + ?.
Passive – Modal auxiliary verb + passive subject + be* + passive object + ?.
Passive – Modal auxiliary verb + passive subject + be* + passive object + ?.
* -Here be itself acts as a be verb.
Examples-
Active – Will he teach us?
Passive – Shall we be taught by him?
Active – Can't you buy a movie ticket?
Passive – Can't a movie ticket be bought by you?
When is 'by' not used and other in passive voice?
# There are some prepositions used in place of 'by' after certain verbs.Like,
E.g.-
Active – Her skill astonishes the audience.
Passive – The audience are astonished at her skill.
"... by her skill."❌
Active – We know the cheater.
Passive – The cheater is known to us.
Active – Her salary does not satisfy her luxurious lifestyle.
Passive – Her luxurious lifestyle is not satisfied with her salary.
Active – His magic trick has pleased us.
Passive – We have been pleased with his magic trick.
Active – His behaviour surprised the teachers.
Passive – The teachers were surprised at his behaviour.
Active – Does her conduct annoy you?
Passive – Are you annoyed at her conduct?
| Verbs | Suitable Prepositions | Verbs | Suitable Prepositions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Astonished | at | Invited | to |
| Amazed | at | Compared | to |
| Annoyed | at | Distinguished | with |
| Knocked | at | Preferred | for |
| Prepared | for | Satisfied | with |
| Interested | in | Pleased | with |
| Addicted | to | Disgusted | with |
| Known | to | Quarrelled | with |
E.g.-
Active – Her skill astonishes the audience.
Passive – The audience are astonished at her skill.
"... by her skill."❌
Active – We know the cheater.
Passive – The cheater is known to us.
Active – Her salary does not satisfy her luxurious lifestyle.
Passive – Her luxurious lifestyle is not satisfied with her salary.
Active – His magic trick has pleased us.
Passive – We have been pleased with his magic trick.
Active – His behaviour surprised the teachers.
Passive – The teachers were surprised at his behaviour.
Active – Does her conduct annoy you?
Passive – Are you annoyed at her conduct?
Thank you...




%20(1).webp)


%20(1).webp)
3 Comments
Thanks alot for this stupendous, astonishing, well teached information
ReplyDeleteThat helped me alot in learning
Active and passive voice...l love it
Thanks alot for this stupendous, astonishing, well teached information
ReplyDeleteThat helped me alot in learning
Active and passive voice...l love it
Would like to thank the creator/creators of this site. Grammar structure well documented.I found it very useful.Thanks again for all the effort you have gone through to make this format.
ReplyDeleteLeave a comment